
SpringBoot入门
本文最后更新于 2024-03-23,欢迎来到我的Blog! https://www.zpeng.site/
1.SpringBoot入门
1.1.POM文件
1.1.1.父项目
<!--1、SpringBoot的pom文件中导入父项目-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<!--2、spring-boot-starter-parent的父项目是spring-boot-dependencies
spring-boot-dependencies 定义很多jar的版本,它是真正来管理SpringBoot应用里所有依赖的版本!
-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>spring-boot-dependencies是SpringBoot应用版本仲裁中心!以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本的!没有在
spring-boot-dependencies管理的依赖我们自然需要声明版本号。
1.1.1.启动器(starter)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>spring-boot-starter-==web==:spring-boot-starter是SpringBoot场景启动器。
spring-boot-starter-web帮我导入了Web模块需要正常运行的组件。一句话:SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter(启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些starter相关场景的所有依赖都会导入进来!要用什么功能就导入什么starter(启动器)即可。
1.2.自动配置
1.2.1.@SpringBootApplication
主配置类
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类,说明这是一个SpringBoot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class ApplicationJD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApplicationJD.class, args);
}
}@SpringBootApplication:该注解标注在某个类上说明,这个类是SpringBoot应用的主配置类,就可以运行主配置类的main()方法来启动SpringBoot应用!
@SpringBootApplication 是一个组合注解,主要由@SpringBootConfiguration和@EnableAutoConfiguration组成。
1.2.2.@SpringBootConfiguration
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 是一个组合注解,该注解表示SpringBoot的配置类。
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* @SpringBootConfiguration 是由@Configuration组成的
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {@SpringBootConfiguration:该注解表示SpringBoot的配置类。
@SpringBootConfiguration标注在某个类上,表示这是一个SpringBoot配置类。
@SpringBootConfiguration由@Configuration注解组成的,@Configuration也是代表配置类。
只不过@SpringBootConfiguration是SpringBoot定义的注解,@Configuration是Spring定义的注解。
注意:@Configuration是由@Component组成的,标注@Configuration的类也是Spring容器的一个组件。
1.2.3.@EnableAutoConfiguration
/**
* @EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能
* 以前我们需要配置的东西,SpringBoot帮我们配置,@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,这样自动置才能生效。
* @EnableAutoConfiguration 由 @AutoConfigurationPackage 和 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)组成。
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
/**
* @AutoConfigurationPackage
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包。
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class):@import是Spring的底层注解,给容器导入组件。
一句话:@AutoConfigurationPackage就是将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的这个类)的所在包及下面所有子包和所有组件扫描到SpringBoot容器中。
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):给容器导入组件。
AutoConfigurationImportSelector:这个类是给容器导入组件的选择器。将需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器中。
一句话:(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class会给SpringBoot导入非常多的配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration),这些自动配置类会给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件。
1.2.4.总结
@SpringBootApplication:主配置类 + 包扫描 + 导入xxxAutoConfiguration配置类。@SpringBootConfiguration:SpringBoot声明的配置类。@Configuration:Spring声明的配置类,也是一个组件@Component。
@EnableAutoConfiguration:包扫描 + 导入xxxAutoConfiguration配置类。@AutoConfigurationPackage:包扫描。@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):SpringBoot在启动时从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,再将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效了。
2.配置文件
2.1.配置文件介绍
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件的名字是固定的:
application.properties和application.yml。配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值。
application.properties和application.yml一般都放在src/main/resources目录下。
2.2.YAML语法
基本语法
# 1、key: value表示一对键值对(中间的空格必须有!)
# 2、以空格的缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的。
# 属性和值也是大小写敏感的!
server:
port: 1997值的写法
# 1、普通的值(数字、字符串、布尔)
# key: value 直接写就可以
# 字符串默认不用加单引号/双引号。
# 双引号:会转义字符串里面的特殊字符。
name: "zhangsan \n lisi" # zhangsan 换行 lisi
# 单引号:不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符。单引号就是原样输出!
name: 'zhangsan \n lisi' # zhangsan \n lisi
# 2、对象和Map(属性和值/键值对)
# 对象就是k: v Map和对象的写法相似
# 只是注意空格和缩进就可以了!
friends:
name: zhangsan
age: 18
addr: beijing
# 3、数组(List、Set)
# 数组用"- "来表示数组中的一个元素
pets:
- cat:
name: tom
- dog
name: ErHa2.3.配置文件值的注入
2.3.1.@ConfigurationProperties
Person类
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @ConfigurationProperties默认从全局配置文件中获取值。
* @ConfigurationProperties 将配置文件中每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中。
* @ConfigurationProperties 告诉SpringBoot将实体类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
* prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行映射
*
* @Component: 需要把entity加入到容器中才能把yml的值映射到实体类中
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private boolean sex;
private Date birth;
private Map<String, Object> map;
private List<Object> list;
private Dog dog;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=" + sex +
", birth=" + birth +
", map=" + map +
", list=" + list +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
}Dog类
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}依赖
<!--导入配置文件处理器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>application.yaml
person:
# 普通的key-value
name: zhangsan
age: 18
sex: true
birth: 2020/7/7
# Map
map:
k1: v1
k2: v2
k3: v3
# List
list:
- list01
- list02
- list03
# 对象
dog:
name: tom
age: 3测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ConfigurationMappingTest {
@Autowired
private Person person;
/**
* 测试application.yaml配置文件值映射到整个实体类中的字段
*/
@Test
public void yamlToEntityAll() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}2.3.2@Value
@Value的使用
public class Person {
/**
* 从配置文件中获取值
*/
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
/**
* Spring计算表达式
*/
@Value("#{11 * 2}")
private Integer age;
/**
* 直接赋值
*/
@Value("true")
private boolean sex;
}2.3.3.@ConfigurationProperties和@Value的区别
松散绑定:firstName可以在配置文件中使用first-name。
一句话:如果我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取配置文件中的某项值,就使用@Value。如果我们专门编写了一个JavaBean来和配置文件进行映射,那么就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties。
2.3.4.JSR303数据校验
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated // 开始JSR303数据校验
public class Person {
/**
* @Email 表示name字段必须填写成邮箱格式
*/
@Email
private String name;2.3.5.@PropertySource
@PropertySource:用于加载指定的配置文件。
@ConfigurationProperties默认从全局配置文件(application.yml)中获取值。
写person.properties配置文件
person.name=zhangsan
person.age=18
person.sex=false使用@PropertySource注解
/**
* @PropertySource 只能读取到properties文件中的配置,不能读取到yaml文件的配置
* @PropertySource 的value是一个数组,可以读取多个指定的配置文件
*/
@Component
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private boolean sex;
}2.3.6.@ImportResource
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效。
SpringBoot中没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,SpringBoot也不能自动识别。想让Spring的配置文件加载进SpringBoot中,使用@ImportResource标注在配置上即可。
这种为SpringBoot添加组件的方式SpringBoot并不推荐。
// 导入Spring的配置文件使其生效
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})2.3.7.@Bean
SpringBoot推荐使用全注解的方式来给Spring容器添加组件!
/**
* @Configuration: 该注解指明当前类是一个配置类,替代Spring的xml配置文件!
* 在Spring的xml配置文件中使用<bean><bean/>标签来添加组件。
* 在@Configuration配置类中使用@Bean注解就可以添加组件。
*/
@Configuration
public class AppMainConf {
/**
* @Bean: 将方法的返回值添加到Spring容器中。这个组件默认的id就是方法名!
*/
@Bean
public HelloService helloService() {
System.out.println("*********配置类给容器中添加helloService组件了*********");
return new HelloService();
}
}2.4.配置文件占位符
# 1、占位符可以使用随机数
# 2、占位符也可以引用之前的值
person:
name: zhangsan${random.uuid} # 随机字符串
age: ${random.int} # 随机的整数
dog:
name: ${person.name} # 引用上面的值2.5.profile多环境支持
profile是Spring対不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活、指定参数等方式快速切换环境。
多Profile文件
# 我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
# 在默认情况下使用的application.yml的配置
# application-dev.yml开发环境配置
server:
port: 8081
# application-prod.yml生产环境配置
server:
port: 8082
# application.yml主配置文件中激活指定配置文件,这样SpringBoot项目就会使用dev环境的配置文件了
spring:
profiles:
active: dev yaml文件支持多文档块方式
server:
port: 8080
# 激活dev开发环境
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
# 开发环境
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles: dev
---
# 生产环境
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: prod命令行方式指定配置文件
java -jar [jar的名字] --spring.profiles.active=dev2.6.配置文件的加载顺序
# 1、配置文件的优先级从高到低
# 所有位置的配置文件SpringBoot都会被加载,高优先级配置内容会覆盖低优先级配置的内容(覆盖的相同的配置)
# 这四个配置文件都会被SpringBoot加载,不同的配置会形成互补配置!
file:/config/application.yml # 当前项目下的config文件夹下的配置文件
file:/application.yml # 当前项目下的配置文件
classpath:/config/application.yml # resources目录下的config文件夹下的配置文件
classpath:/application.yml # resources目录下的配置文件
# 2、项目打包之后可以通过spring.config.location命令行来改变默认的配置文件位置
# 所有的配置文件都会被加载并且都会起作用,形成互补配置
java -jar [jar的名字] --spring.config.location=C:\Users\14666\Desktop3.自动配置
3.1.自动配置原理
//以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration为例来学习SpringBoot的自动配置
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) // 表示这是一个配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpProperties.class) // 启用ConfigurationProperties功能,将配置文件中对应的值和HttpProperties绑定起来。
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET) // Spring底层注解@Conditional,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类才会生效。判断当前应用是否是Web应用!如果是web应用,当前配置类生效。
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) // 判断当前项目是否有CharacterEncodingFilter这个类
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在"spring.http.encoding"这个个配置,matchIfMissing = true如果不存在也是默认存在的。如果配置文件中不配置spring.http.encoding,这个配置类也是生效的!
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在【xxxProperties】类中封装,配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类。
XXXAutoConfiguration是自动配置类,它会给容器中添加组件,然后也会对应的XXXProperties,封装配置文件的相关属性。
3.2.@Conditional
@Conditional是Spring中的注解,作用是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置类里面的所有内容才会生效。
一句话:自动配置类必须在一定条件下才能生效。
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效??
# 1、在SpringBoot的配置文件中加入如下配置就可以打印出自动配置报告
debug: true
# 2、在应用启动的时候就会出现"项目评估报告",就可以查看启用了哪些AutoConfiguration
============================
CONDITIONS EVALUATION REPORT
============================
Positive matches:
-----------------
AopAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.auto=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration.ClassProxyingConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class 'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
- @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition)
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet' (OnClassCondition)
- found 'session' scope (OnWebApplicationCondition)
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.DispatcherServletConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'javax.servlet.ServletRegistration' (OnClassCondition)
- Default DispatcherServlet did not find dispatcher servlet beans (DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.DefaultDispatcherServletCondition)
4.日志
4.1.日志框架
左边选一个日志门面(抽象层),右边选一个来实现!
日志框架的选择:
日志门面:SLF4j。
日志实现:Logback。
SpringBoot底层是Spring框架,Spring框架默认使用
JCL;SpringBoot选用的日志框架是SLF4j和Logback。
4.2.SLF4j的使用
基本使用
以后开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层的方法。
给系统中导入SLF4j的jar和Logback的jar。
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}4.3.SLF4j的使用原理
SLF4j适配其他日志框架
每一个日志的实现框架都有自己的配置文件。使用SLF4j以后,配置文件还是做成日志实现框架的配置文件。
4.4.统一日志框架
问题:开发A系统使用SLF4j + Logback,但是使用了Spring(Commons-logging)、Hibernate(jBoss-logging)、MyBatis。。。。所以,要统一日志框架!即使是别的日志框架,和A系统一起使用SLF4j和Logback一起输出。
如何让系统所有的日志框架都统一到SLF4j?
1、将系统中其他日志框架先排除。
2、用中间的jar来替换原有的日志框架。
3、我们再来导入SLF4j其他的日志实现。
4.4.SpringBoot日志关系
SpringBoot日志依赖
log4j-to-slf4j、logback-classic、jul-to-slf4j把其他的日志框架转成slf4j。slf4j-api是SpringBoot导入了日志抽象层SLF4J。
如果我们要引入其他框架?一个要把这个框架默认的日志依赖移除掉?
SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j + logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架依赖的日志框架排除掉即可。
4.5.SpringBoot日志使用
日志级别
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class LogTest {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
/**
* 日志的级别由低到高:trace < debug < info < warn < error
* 可以调整项目日志级别,日志就只会在这个级别以后的级别生效。
* SpringBoot默认的日志级别是Info
*/
@Test
public void testLogLevel() {
logger.trace("*****trance日志*****");
logger.debug("*****debug日志*****");
logger.info("*****info日志*****");
logger.warn("*****warn日志*****");
logger.error("*****error日志*****");
}
}日志级别的调整和日志输出的位置
# 1、com.ymy.spring.boot.log 这个包下的日志都会输入出trace和trace以上的日志了!!
logging:
level:
com.ymy.spring.boot.log: trace
# 2、默认情况下日志只会打印到控制台上,配置logging.file.name会在当前项目下输出日志
# 不指定路径会在当前项目下生产日志文件,指定路径会在指定路径下生成日志
file:
name: C:/Users/14666/Desktop/springboot.log
# 3、logging.file.path 生成的日志文件默认为spring.log,只需要写日志文件路径
file:
path: C:/Users/14666/Desktop/log/5.Web开发
5.1.静态资源映射规则
5.1.1.webjars静态资源的映射
关于SpringBoot静态资源的映射规则在WebMvcAutoConfiguration中。
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}静态资源映射规则:
所有
/webjars/**的请求都去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/这个目录下找资源。webjars就是以jar的方式引入静态资源。可以百度搜索webjars,在pom中添加相应的依赖就可以了。
5.1.2.ResourceProperties静态资源映射
ResourceProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };静态资源映射规则:
所有访问
/**的请求都会去classpath:/META-INF/resources/、classpath:/resources/、classpath:/static/、classpath:/public/这些路径下找资源。
测试访问静态资源
浏览器输入http://localhost:8080/asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css就可以访问静态资源。
5.1.3.欢迎页映射规则
静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面,被/**映射。
静态资源文件夹:classpath:/META-INF/resources/、classpath:/resources/、classpath:/static/、classpath:/public/。
浏览器访问localhost:8080/index.html会去静态资源文件夹将下找这个html页面。
5.1.4.图标映射规则
所有的**/favicon.ico都是在静态资源文件夹下找。
5.2.thymeleaf
5.2.1.引入thymeleaf
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>5.2.2.thymeleaf的使用
ThymeleafProperties可以修改thymeleaf的配置。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
// 只要我们把HTML页面放到"classpath:/templates/"下,thymeleaf就能找到
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
// 并且配置了默认的后缀是.html
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";thymeleaf语法
<!--1、导入thymeleaf名称空间-->
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"></html>
<!--2、thymeleaf语法-->
<!--
th:text 将div里面的文本内容设置为我们指定的值;
可以使用[th:任意属性]来替换原生HTML属性的值.
-->
<div th:text="${hello}"></div>
<!--片段包含-->
th:insert
th:replcae
<!--遍历-->
th:each
<!--判断-->
th:if
th:unless
th:switch
th:case
<!--声明变量-->
th:object
th:with
<!--属性修改-->
th:attr
th:attrprepend
th:attrappend
<!--修改指定属性默认值-->
th:value
th:href
th:src
...
<!--修改标签体内容-->
th:text
th:utext 不转义特殊字符
<!--声明片段-->
th:fragment
<!--移除片段-->
th:removethymeleaf表达式语法
1.Simple expressions(表达式语法):
1.1.Variable Expressions: ${...} # 获取变量表达式
(1)获取对象的属性、调用方法;
(2)使用内置的基本对象(${#locale.country})
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
(3)使用内置的工具对象
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs #conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation. #arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
#ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration).
1.2.Selection Variable Expressions: *{...} # 变量的选择表达式,和${}在功能上是一样的,只不过有补充
(1)补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}" 使用
1.3.Message Expressions: #{...} # 获取国际化内容的
1.4.Link URL Expressions: @{...} # 定义URL链接
1.5.Fragment Expressions: ~{...} # 片段引用表达式
2.Literals(字面量):
2.1.Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
2.2.Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
2.3.Boolean literals: true , false
2.4.Null literal: null
2.5.Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
3.Text operations(文本操作):
3.1.String concatenation: +
3.2.Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
4.Arithmetic operations(数学运算):
4.1.Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
4.2.Minus sign (unary operator): -
5.Boolean operations(布尔操作):
5.1.Binary operators: and , or
5.2.Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
6.Comparisons and equality(比较运算):
6.1.Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
6.2.Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
7.Conditional operators(条件运算):
7.1.If-then: (if) ? (then)
7.2.If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
7.3.Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
8.Special tokens(特殊操作):
8.1No-Operation: _5.3.SpringMVC自动配置原理
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.SpringBoot自动配置了ViewResolver,视图解析器,根据方法的返回值得到视图对象,决定如何渲染(转发、重定向)。
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:作用就是组合所有的视图解析器。如何定制视图解析器:我们可以在容器中添加一个
ViewResolver视图解析器,ContentNegotiatingViewResolver就会自动的将我们的视图解析器组合进来
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered later in this document)).
Automatic registration of
Converter,GenericConverter, andFormatterbeans.Converter:转换器,对象类型转换使用Converter组件。Formatter:格式化器,2020-12-17需要转化成日期类型,就需要使用格式化器。自己添加的
Converter和Formatter只需要放在容器中即可。
Support for
HttpMessageConverters(covered later in this document).HttpMessageConverters:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的HttpMessageConverter集合,可以获取容器中所有的HttpMessageConverter`。添加自己的
HttpMessageConverter,只需要将组件加入到容器即可。
Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(covered later in this document).MessageCodesResolver:用来定义错误代码的生成规则。
Static
index.htmlsupport.Custom
Faviconsupport (covered later in this document).Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (covered later in this document).我们可以配置一个
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer添加到容器来替换默认的。@Override protected ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer( FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, Validator mvcValidator) { try { // 从容器中拿ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer return this.beanFactory.getBean(ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer.class); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // 从容器中拿不到就调用父类的方法 return super.getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer(mvcConversionService, mvcValidator); } }ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer:数据绑定器的作用是将请求数据绑定到JavaBean中。
扩展SpringMVC:If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more MVC customizations (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc.
完全接管SpringMVC:If you want to take complete control(完全控制) of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc, or alternatively(或者)add your own @Configuration-annotated DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration as described in the Javadoc of @EnableWebMvc.
If you want to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, and still keep the Spring Boot MVC customizations, you can declare a bean of type WebMvcRegistrations and use it to provide custom instances of those components.
5.4.国际化
5.4.1.编写国际化配置文件
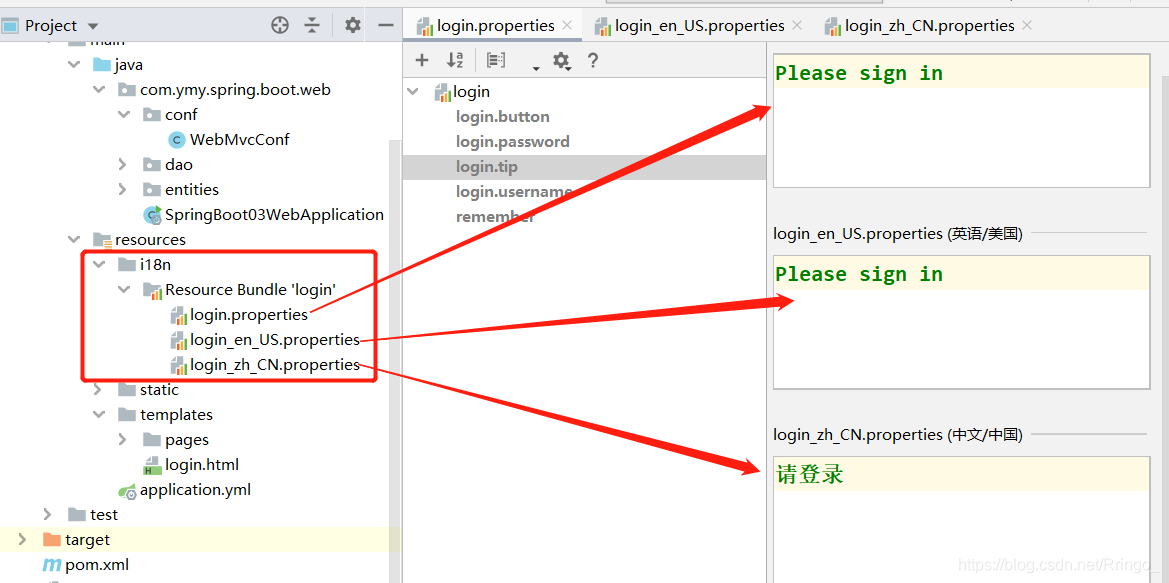
5.4.2.国际化相关的组件
SpringBoot自动配置好了国际化相关的组件
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = AbstractApplicationContext.MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Conditional(ResourceBundleCondition.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
private static final Resource[] NO_RESOURCES = {};
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages")
public MessageSourceProperties messageSourceProperties() {
/* MessageSourceProperties中的basename默认是"message"
* 我们项目中的basename就是login,去掉后面的"语言名"和"国家名"
*/
return new MessageSourceProperties();
}
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource(MessageSourceProperties properties) {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getBasename())) {
// 设置国际化文件的basename
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils
.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(properties.getBasename())));
}
if (properties.getEncoding() != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(properties.getEncoding().name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(properties.isFallbackToSystemLocale());
Duration cacheDuration = properties.getCacheDuration();
if (cacheDuration != null) {
messageSource.setCacheMillis(cacheDuration.toMillis());
}
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(properties.isAlwaysUseMessageFormat());
messageSource.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(properties.isUseCodeAsDefaultMessage());
return messageSource;
}在application.yml中修改SpringBoot国际化相关的basename
spring:
messages:
# 修改basename
basename: i18n.login 去HTML页面获取国际化的值
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.username}">Username</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus="">
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.password}">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required="">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"> [[#{login.remember}]]
</label>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.button}">Sign in</button>5.4.3.区域信息解析器
默认LocaleResolver
// WebMvcAutoConfiguration中配置的区域信息解析器
// 默认的区域信息解析器是根据Http请求的请求头来获取Locale进行国际化
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale")
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
if (this.mvcProperties.getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) {
return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
}
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
return localeResolver;
}自定义LocaleResolver
/**
* 自定义的login.html的区域信息解析器
* 根据请求来解析地区,可以实现点击切换语言的功能
*/
public class LoginLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
// LoginConstant.PARAM_KEY 是 language
String language = request.getParameter(LoginConstant.PARAM_KEY);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)) {
String[] split = language.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
}login.html页面中发送的请求
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(language=zh_CN)}">中文</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(language=en_US)}">English</a>在配置类中添加自定义的区域信息解析器
/**
* 自定义区域信息解析器
* @return
*/
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
return new LoginLocaleResolver();
}5.5.登录拦截器
拦截器
/**
* 登录拦截器
*/
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
Object key = request.getSession().getAttribute(LoginConstant.LOGIN_SESSION_KEY);
if (key == null) {
// 未登录返回到登录页面
request.setAttribute("message", "没有权限,请先登录");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request, response);
return false;
}else {
// 已经登录,方向请求
return true;
}
}
}将拦截器加入容器
/**
* SpringMVC的扩展配置
*/
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConf implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 配置拦截器
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")
// 排除登录、首页、静态资源路径
.excludePathPatterns("/","/index","/index.html", LoginConstant.LOGIN_PATH, "/asserts/**" );
}
}5.6.RESTfulAPI
基本请求模板
实验请求架构
5.7.数据列表展示
5.7.1.thymeleaf公共元素抽取
<!--1、抽取公共片段-->
<div th:fragment="copy">
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</div>
<!--1、插入公共片段-->
~{templatename::fragmentname} :模板名,片段名
<div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}"></div>三种引入公共片段的th属性:
th:insertis the simplest: it will simply insert the specified fragment as the body of its host tag.将公共片段整个插入到声明的元素中。
th:replaceactually replaces its host tag with the specified fragment.将声明的元素替换为公共片段。
th:includeis similar to th:insert , but instead of inserting the fragment it only inserts the contents of this fragment.将公共片段的内容包含到声明的元素中
<!--抽取的公共片段-->
<footer th:fragment="copy">
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</footer>
<!--三种引入公共片段的方式-->
<body>
...
<div th:insert="footer :: copy"></div>
<div th:replace="footer :: copy"></div>
<div th:include="footer :: copy"></div>
</body>
<!--三种方式的效果-->
<body>
...
<div>
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</footer>
</div>
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</footer>
<div>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</div>
</body5.8.2.SideBar链接高亮
<!--1、sidebar片段加入判断!-->
<li class="nav-item">
<a th:href="@{/main.html}"
th:class="${activeUri=='main.html' ? 'nav-link active' : 'nav-link'}">
Dashboard
</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a th:href="@{/emps}"
th:class="${activeUri=='emps' ? 'nav-link active' : 'nav-link'}">
员工管理
</a>
</li>
<!--2、DashBoard引入sidebar添加activeUri='main.html'-->
<div th:replace="fragments/SideBar :: sidebar(activeUri='main.html')"></div>
<!--3、list引入sidebar添加activeUri='emps'-->
<div th:replace="fragments/SideBar :: sidebar(activeUri='emps')"></div>5.8.日期格式
日期格式有2020-7-10,2020/7/10,2020.7.10;SpringMVC将页面提交的值需要转换为指定的类型;
SpringMVC默认是使用2020/7/10的格式。
# 修改SpringMVC默认的日期格式 yaml修改即可
spring:
mvc:
date-format: yyyy-MM-dd6.错误处理机制
6.1.SpringBoot默认错误处理机制
浏览器访问,默认返回一个错误页面。
如果是APP访问,默认响应一个json数据
原理:参照
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration。给容器添加了以下组件// DefaultErrorAttributes 帮我们在页面共享信息 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() { return new DefaultErrorAttributes(this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException()); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) { return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(), errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList())); } @Bean public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) { return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath); } @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(ErrorViewResolver.class) DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() { return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext, this.resourceProperties); }执行步骤
// 1、一旦出现4xx或者5xx的错误ErrorPageCustomizer(定制错误的响应规则)就会生效。 // ErrorPageCustomizer会拿到path。 @Value("${error.path:/error}") private String path = "/error"; // 系统出现错误后会来到/error请求进行处理 // 2、BasicErrorController处理默认/error请求 @Controller @RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}") public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController { // MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE = "text/html" // 该方法就是产生HTML的数据 // 浏览器发送的请求来到这个方法处理 @RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); Map<String, Object> model = Collections .unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); response.setStatus(status.value()); // 去哪个页面作为错误页面,包含页面地址和页面内容 ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model); } protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status,Map<String, Object> model) { // 所有的ErrorViewResolver得到ModelAndView for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) { ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model); if (modelAndView != null) { return modelAndView; } } return null; } // 产生json数据 // 其他客户端发送的请求来到这个方法处理 @RequestMapping public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) { return new ResponseEntity<>(status); } Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL)); return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status); } } // 3、DefaultErrorViewResolver来得到ModelAndview public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered { private static final Map<Series, String> SERIES_VIEWS; static { Map<Series, String> views = new EnumMap<>(Series.class); views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx"); views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx"); SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views); } @Override public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) { ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model); if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) { modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model); } return modelAndView; } private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) { // SpringBoot可以在error目录下找到页面 String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName; // 如果模板引擎能解析这个地址,就用模板引擎解析 TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext); if (provider != null) { // 模板引擎可用的情况下返回到指定view视图地址 return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model); } // 模板引擎不可用调用resolveResource(),在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName对应的页面 error/404.html return resolveResource(errorViewName, model); } private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) { for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) { try { Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location); resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html"); if (resource.exists()) { return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model); } } catch (Exception ex) { } } return null; } }
6.2.如何定制错误的响应?
6.2.1定制错误页面
有模板引擎的情况下,直接在
templates下创建error文件夹。error文件夹下面的HttpStatus.html(需要用状态码给错误页面命名)就可以被解析返回给浏览器。错误页面可以获取到的信息?
DefaultErrorAttributes可以帮我们在页面获取信息!@Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // 1、可以在错误页面获取到时间戳 errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date()); // 2、可以在错误页面获取到状态码 addStatus(errorAttributes, webRequest); // 1、可以在错误页面获取到错误信息 Exception对象 Exception的Message Errors(JSR303数据校验的信息) addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, webRequest, includeStackTrace); addPath(errorAttributes, webRequest); return errorAttributes; }
没有模板引擎,就会在静态资源文件夹下找error/404.html。
模板引擎和静态资源文件夹下都没有自己写的错误页面,就会来到SpringBoot默认的错误页面。
6.2.2.定制错误数据
@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public String handelException(HttpServletRequest request, Exception ex) {
// 传入我们自己的状态码,这个一定要写
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code", 400);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("tip", "自定义的全局异常处理器");
// 将Map放在请求域中
request.setAttribute("ext", map);
return "forward:/error";
}
}将我们定制的错误信息携带出去
package com.ymy.spring.boot.web.component;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import java.util.Map;
// 自己写的ErrorAttributes
@Component
public class MyErrorAttribute extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
// 可以从请求域中获取map
Map ext = (Map)webRequest.getAttribute("ext", RequestAttributes.SCOPE_REQUEST);
map.put("ext", ext);
return map;
}
}7.数据访问
7.1.Spring Data简介
对于数据访问层,无论是SQL还是NoSQL ,Spring Boot默认采用整合Spring Data的方式进行统一管理,添加大量自动配置,屏蔽了很多设置。引入各种Template,Repository来简化我们対数据访问层的操作。对我们来说只需要进行简单的设置即可。
7.2.JDBC
依赖
<!--jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>application.yml配置
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 333
url: jdbc:mysql://39.97.3.60:3306/jdbc?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
type: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlConnectionPoolDataSource7.3.Druid
依赖
<!--druid-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>${druid.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>配置Druid
# application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 333
url: jdbc:mysql://39.97.3.60:3306/jdbc?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#最大连接池数量
max-active: 20
#初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法,或者第一次getConnection时
initial-size: 10
# 获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,
# 并发效率会有所下降,如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
max-wait: 60000
#最小连接池数量
min-idle: 5
#有两个含义:
#1: Destroy线程会检测连接的间隔时间
#2: testWhileIdle的判断依据,详细看testWhileIdle属性的说明
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
#配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 180000
#用来检测连接是否有效的sql,要求是一个查询语句。如果validationQuery为null,testOnBorrow、testOnReturn、testWhileIdle都不会其作用。
validation-query: select 'x'
#连接有效性检查的超时时间 1 秒
validation-query-timeout: 1
#申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。
test-on-borrow: false
#设置从连接池获取连接时是否检查连接有效性,true时,如果连接空闲时间超过minEvictableIdleTimeMillis进行检查,否则不检查;false时,不检查
test-while-idle: true
#归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能
test-on-return: false
#是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。
pool-prepared-statements: true
#要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,
# 不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
max-open-prepared-statements: 20
#数据库链接超过3分钟开始关闭空闲连接 秒为单位
remove-abandoned-timeout: 1800
#对于长时间不使用的连接强制关闭
remove-abandoned: true
#打开后,增强timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis的周期性连接检查,minIdle内的空闲连接,
keep-alive: true
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
connect-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000
#是否超时关闭连接 默认为false ,若为true 就算数据库恢复连接,也无法连接上
break-after-acquire-failure: false
#设置获取连接出错时的自动重连次数
connection-error-retry-attempts: 1
#设置获取连接时的重试次数,-1为不重试
not-full-fimeout-retry-count: 2
#重连间隔时间 单位毫秒
acquire-retry-delay: 10000
# 设置获取连接出错时是否马上返回错误,true为马上返回
fail-fast: true
#属性类型是字符串,通过别名的方式配置扩展插件,常用的插件有:
#监控统计用的filter:stat日志用的filter:log4j防御sql注入的filter:wall
filters: stat,wallDruid的配置
@Configuration
public class DruidConf {
/**
* 配置Druid的监控Servlet
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin");
initParams.put("loginPassword", "admin");
initParams.put("allow", ""); // 默认就是允许所有
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
/**
* 配置一个Web监控的Filter
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return bean;
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource druidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}7.4.MyBatis
依赖
<properties>
<mybatis.spring.boot.starter.version>2.1.1</mybatis.spring.boot.starter.version>
</properties>
<!--mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.spring.boot.starter.version}</version>
</dependency>application.yml
mybatis:
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-conf.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xmlmyBatis全局配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
</configuration>mapper映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.ymy.spring.boot.mapper.DepartmentMapper">
</mapper>7.5.JPA
7.5.1.SpringData
7.5.2.整合JPA
实例类和数据表进行映射
import javax.persistence.*;
/**
* @Entity 告诉jpa这是一个实体类,和数据表映射的类
* @Table 来指定和哪个数据表对应,如果省略默认就是命令就是user
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "tbl_user")
public class User {
@Id // 表示该字段是主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) // 主键自增
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "last_name", length = 50) // 和数据表对应的一个列
private String lastName;
@Column // 省略默认类名就是属性名
private String email;编写实例类对应的Dao接口
import com.ymy.spring.boot.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
/**
* UserRepository继承JpaRepository<实体类,主键类型>
*/
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {
}基本配置
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 333
url: jdbc:mysql://39.97.3.60:3306/jpa?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
type: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlConnectionPoolDataSource
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update # 更新或者创建数据表
show-sql: true # 在控制台显示sql启动应用的时候,就会自动在数据库中创建表了!
JPA的基本使用
import com.ymy.spring.boot.entity.User;
import com.ymy.spring.boot.repository.UserRepository;
import com.ymy.spring.boot.support.SimpleResponse;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public SimpleResponse getUser(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
try{
User user = userRepository.findById(id).get();
return new SimpleResponse(HttpStatus.OK.value(),"查询成功", user);
}catch (Exception e){
return new SimpleResponse(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(),"没有查到", null);
}
}
@PostMapping("/user")
public SimpleResponse insertUser(@RequestBody User user) {
User save = userRepository.save(user);
if (save != null) {
return new SimpleResponse(HttpStatus.OK.value(),"插入成功", save);
}
return new SimpleResponse(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(),"插入失败", save);
}
}8.SpringBoot事件监听
配置四个监听器:
ApplicationContextInitializer(要写在META-INF/spring.factories中)
ApplicationRunner(直接加入到容器中)
CommandLineRunner(直接加入到容器中)
SpringApplicationRunListener(要写在META-INF/spring.factories中)
// 1.ApplicationContextInitializer
public class HelloApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
System.out.println("*****ApplicationContextInitializer*****" + applicationContext);
}
}
// 2.ApplicationRunner
@Component
public class HelloApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("****ApplicationRunner***run");
}
}
// 3.CommandLineRunner
@Component
public class HelloCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("****HelloCommandLineRunner****");
}
}
// 4.SpringApplicationRunListener
public class HelloSpringApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
public HelloSpringApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
}
@Override
public void starting() {
System.out.println("*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****starting");
}
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
Object osName = environment.getSystemProperties().get("os.name");
System.out.println("*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****environmentPrepared " + osName);
}
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****contextPrepared");
}
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****contextLoaded");
}
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****started");
}
@Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****running");
}
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
System.out.println("*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****failed");
}
}控制台输出顺序
*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****starting
*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****environmentPrepared Windows 10
*****ApplicationContextInitializer*****
*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****contextPrepared
*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****contextLoaded
*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****started
****ApplicationRunner***run
****CommandLineRunner****
*****SpringApplicationRunListener*****running9.自定义Starter
9.1.基本介绍
starter:
这个场景需要使用到的依赖是什么?
如果编写自动配置?
@Configuration // 指定这个类是个配置类
@ConditionalOnXXX // 在指定条件成立的情况下自动配置类生效
@AutoConfigureAfter // 指定自动配置类的顺序
@Bean // 给容器中添加组件
@ConfigurationPropertis // 结合Properties类来绑定相关的配置
@EnableConfigurationProperties // 让xxxProperties生效并加入到容器中
自动配置类要能加载
将需要启动就加载的自动配置类,配置在META-INF/spring.factories9.2.模式介绍
启动器只用来做依赖导入。
专门来写一个自动配置模块。
启动器依赖自动配置,别人只需要引入启动器(starter),自动配置就配置好了
starter的命名:
mybatis-spring-boot-starter,自定义启动器名-spring-boot-starter。
9.3.自动配置模块
pom
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ymy</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-08-autoconfiguration</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--引入spring-boot-starter 所有starter的基本配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--导入配置文件处理器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>HelloProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "ymy.hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
public String getPrefix() {
return prefix;
}
public void setPrefix(String prefix) {
this.prefix = prefix;
}
public String getSuffix() {
return suffix;
}
public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
this.suffix = suffix;
}
}HelloService
public class HelloService {
private HelloProperties helloProperties;
public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() {
return helloProperties;
}
public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
public String sayHello(String name) {
return helloProperties.getPrefix() + name + helloProperties.getSuffix();
}
}自动配置
package com.ymy.spring.boot.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication // web应用才生效
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = HelloProperties.class)
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private HelloProperties helloProperties;
// 这样就把HelloService组件加入了容器,并且可以在yml中配置
@Bean
public HelloService helloService() {
HelloService helloService = new HelloService();
helloService.setHelloProperties(helloProperties);
return helloService;
}
}spring.factories
# 在resources目录下创建spring.factories文件
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.ymy.spring.boot.service.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration9.4.自定义starter
自定义starter需要把我们写的自动配置模块导入进来并且安装到本地仓库,就可以让其他项目来使用了!
10.SpringBoot与缓存
10.1.核心概念
10.2.缓存的使用
步骤
开启注解的缓存
@EnableCaching。在方法上标注缓存注解
@Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut。
缓存的SpEL表达式
@cacheable
import com.ymy.spring.boot.cache.entity.Employee;
import com.ymy.spring.boot.cache.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.ymy.spring.boot.cache.support.SimpleResponse;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Resource
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
* @Cacheable 将方法的运行结果进行缓存,以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法。
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件,每个缓存组件有自己唯一的名字。
*
* 运行时机:先查缓存,再运行目标方法。
*
* @Cacheable 的属性:
* value/cacheNames:指定缓存的名字。
* key:缓存数据时使用的key。默认是使用方法参数的值! key = "#id" 可以使用SpEL表达式。
* keyGenerator:可以自己指定key的生成器。(key和keyGenerator二选一使用)。
* cacheManager:指定缓存管理器。
* cacheResolver:指定缓存解析器。(cacheManager和cacheResolver二选一)。
* condition:指定符合条件的情况下,才进行缓存。
* unless:否定缓存。当unless的条件为true,就不会缓存。(unless和condition用法相反)。
* sync:是否使用同步模式。
*
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"employee"}, key = "#root.args[0]")
public SimpleResponse getEmployeeById(Integer id) {
Employee employee = employeeMapper.getEmployeeById(id);
if (employee == null) {
return new SimpleResponse(404, "数据库没有该员工!", null);
}
return new SimpleResponse(200, "查询成功", employee);
}
}@CachePut
/**
* @CachePut 既调用方法又更新缓存数据。
* 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存
* 运行时机:
* 1.先调用目标方法
* 2.将目标方法的结果缓存起来
*/
@CachePut(cacheNames = {"employee"}, key = "#employee.id")
public SimpleResponse updateEmployee(Employee employee) {
Integer ret = employeeMapper.updateEmployee(employee);
if (ret > 0) {
return new SimpleResponse(200, "修改成功",
employeeMapper.getEmployeeById(employee.getId()));
}
return new SimpleResponse(500, "修改失败", null);
}@CacheEvict
/**
* @CacheEvict 缓存清除
*
* key:指定要清除的缓存的key。
* allEntries:是否清除所有缓存。默认是false。
* beforeInvocation:缓存的清除是否在方法执行之前清除。默认是false,代表在方法执行之后才清除缓存。
* beforeInvocation=true:无论目标方法是否异常。缓存都会被清除!
*/
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = {"employee"}, key = "#id", beforeInvocation = true)
public SimpleResponse deleteEmployee(Integer id) {
Integer ret = employeeMapper.deleteEmployee(id);
if (ret > 0) {
return new SimpleResponse(200, "删除成功", ret);
}
return new SimpleResponse(500, "删除失败", ret);
}10.3.缓存工作原理
// 1、缓存的配置类
0 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration"
1 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration"
2 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration"
3 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration"
4 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration"
5 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration"
6 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration"
7 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration"
8 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration"
9 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration"
// 2、SpringBoot默认使用的是SimpleCacheConfiguration
SimpleCacheConfiguration matched:
- Cache org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration automatic cache type (CacheCondition)
- @ConditionalOnBean (types: org.springframework.cache.CacheManager; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans (OnBeanCondition)
// 3、SimpleCacheConfiguration给容器中加入了ConcurrentMapCacheManager
ConcurrentMapCacheManager可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的组件
// 4、缓存的运行流程
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
synchronized (this.cacheMap) {
cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
(1)目标方法在发送SQL之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照CacheNames指定的名字获取。CacheManager先获取相应的缓存,第一次获取如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。
(2)去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数名。key是按照某种策略生成的。
(3)没有查到缓存就调用目标方法。
(4)将目标方法返回的结果放到缓存中。10.4.自定义KeyGenerator
定义KeyGenerator
@Configuration
public class CacheConf {
@Bean(name = "myKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
return method.getName() + "[" + Arrays.asList(params).toString() + "]";
}
};
}
}使用KeyGenerator
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"employee"}, keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator")
public SimpleResponse getEmployeeById(Integer id) {
Employee employee = employeeMapper.getEmployeeById(id);
if (employee == null) {
return new SimpleResponse(404, "数据库没有该员工!", null);
}
return new SimpleResponse(200, "查询成功", employee);
}10.5.Redis缓存
依赖
<!--redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>导入Redis依赖,SpringBoot缓存就使用了Redis。
配置RedisCacheManager
package com.ymy.spring.boot.cache.conf;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.jsontype.impl.LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.time.Duration;
@Configuration
public class RedisConf {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
objectMapper.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题)
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}11.定时任务
@Service
public class ScheduledService {
/**
* @Scheduled 定时任务
* second, minute, hour, day of month, month, and day of week
* 0 * * * * MON-TUE:任意月的星期二的每个整分钟都会调用一次该方法
*/
@Scheduled(cron = "0 * * * * MON-TUE")
public void hello() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
@EnableScheduling // @EnableScheduling需要开启定时任务功能!
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBoot10TaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot10TaskApplication.class, args);
}
}cron表达式
特殊字符的含义
@Scheduled属性:
fixedDelay:上一个任务结束和下一个任务开始的间隔时间(单位毫秒)。fixedRate:两次定时任务开始的时间间隔。initialDelay:在第一个定时任务执行之前,需要延迟的时间。
12.邮件任务
12.1. 依赖和配置
<!--mail-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>配置
spring:
mail:
username: 1466637477@qq.com # 配置发送的邮箱
password: oexnnqprsuqngcbj # 配置邮箱的授权码
host: smtp.qq.com # 邮箱服务器地址
default-encoding: UTF-8
port: 587spring.mail.properties.mail.stmp.socketFactory.class=javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory
spring.mail.properties.mail.debug=true12.2. 简单邮件
@Resource
private JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
@Test
public void senderSimpleEmail() {
SimpleMailMessage mail = new SimpleMailMessage();
// 邮件的标题
mail.setSubject("测试发送邮件");
// 邮件的内容
mail.setText("********测试********");
// 邮件发送给谁
mail.setTo("YmyLearning@163.com");
// 谁发送的!
mail.setFrom("1466637477@qq.com");
mailSender.send(mail);
}12.3. 复杂邮件
@Resource
private JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
@Test
public void senderEmail() throws Exception{
// 1、创建一个复杂的消息邮件
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
// multipart为true 表示要上传文件
MimeMessageHelper mimeMessageHelper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true);
// 2、设计邮件内容
mimeMessageHelper.setSubject("测试发送复杂邮件");
mimeMessageHelper.setText("<b>今天7点30开会</b>", true);
mimeMessageHelper.addAttachment("毕业声登记表.pdf", new File("C:\\Users\\14666\\Desktop\\毕业声登记表.pdf"));
mimeMessageHelper.setTo("YmyLearning@163.com");
mimeMessageHelper.setFrom("1466637477@qq.com");
// 3、发送邮件
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}12.4. Thymeleaf邮件模板
(1)依赖
<!-- thymeleaf -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>(2)HTML模板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>邮件模板</title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.w {
width: 800px;
margin: 20px auto;
}
.tab,
.tab td,
.tab th {
border: 1px solid pink;
text-align: center;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="w">
<!-- 注意:引用一定要写 ${xxx} -->
<h4>
Hello <span th:text="${username}"></span>, 欢迎来到xxx大家庭!
</h4>
<div>
<h5>您的入职信息如下!</h5>
<table class="tab">
<tr>
<td>职位:</td>
<td th:text="${position}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>薪水:</td>
<td th:text="${salary}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>部门:</td>
<td th:text="${department}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>(3)发送邮件
/**
* @author Ringo
* @since 2021/4/13 11:45
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class MainTest {
// 发送邮件
@Resource
private JavaMailSender mailSender;
// Thymeleaf 模板引擎
@Resource
private SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine;
@Autowired
private MailProperties mailProperties;
@Test
void sendMail() throws Exception {
MimeMessage message = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(message, true);
// 1: 解析 Thymeleaf 模板
Context context = new Context();
context.setVariable("username", "Ringo");
context.setVariable("position", "Java工程师");
context.setVariable("department", "技术部");
context.setVariable("salary", "8000");
String process = templateEngine.process("Mail.html", context);
// 2: 设置邮件内容
helper.setSubject("测试邮件主题");
helper.setText(process, true);
helper.setSentDate(new Date());
helper.setTo("594707128@qq.com");
helper.setFrom(mailProperties.getUsername());
// 3: 发送邮件
mailSender.send(message);
}
}- 感谢你赐予我前进的力量



